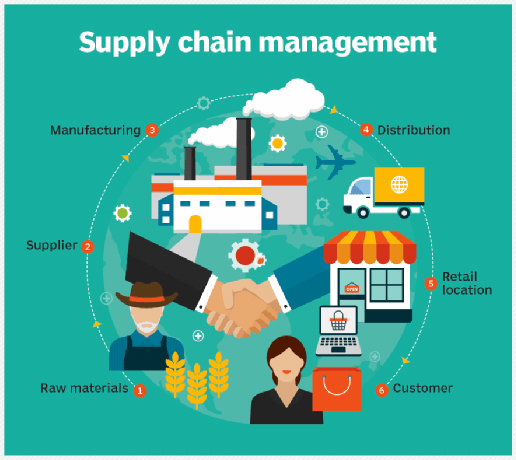
Introduction
- Eligibility: 10+2 from any recognized Indian/ State board
- Duration of the Course: One-Year
- The Diploma in Supply chain management is a one-year program for 10+2 students who wants build their career in the supply chain area. Many online aggregators like Amazon, Bigbazar, Flip cart, Big Basket and many more are in the business and needs trained manpower for running their businesses. With liberalization, and simplification of trade policies, it is relatively a lot easier for someone to get into the supply chain part of business houses. The course thus lays emphasis on the various aspects of supply chain process.
- Examination: As per the university rules, there will be provision of internal assessment for each paper which will carry 40% weight age. The final term-end examination will be held on semester basis and will carry 60% weight age
Selection & Fee: Selection will be on the basis of merit cum interview. Fee is Rs.25000 payable at the time of admission.
DIPLOMA IN SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT (DSM)
- Duration of the Course: One-Year
- Eligibility: Eligibility: 10+2 from any recognized Indian/ state board
Examination: As per the university rules, there will be provision of internal assessment for each paper which will carry 40% weight age. The final term-end examination will be held on semester basis and will carry 60% weight age
Semester I
DSM-101 Accounting and Mathematics for Management
DSM-102 Business Economics, Environment and Regulatory Framework
DSM-103 Introduction to Supply Chain Management and Logistics
DSM-104 Materials and Inventory in Supply Chain Management
DSM-105 Seminars and presentations
Semester II
DSM-106 Transportation, Warehousing and Freight Management
DSM-107 Supply Chain Service Practice and Procedure
DSM-108 Global Supply Chain, Export Trade and documentation
DSM-109 Computer Application in Supply Chain Management
DSM-110 Industrial Training, project report, and presentation
COURSE CURRICULUM AND STRUCTURE
| S. No. | Module | Course code | Course Name | Credits | Contact hours |
Marks-100 (External /Internal) |
| Semester I | ||||||
| 1 | Module 1 | DSM-101 | Accounting and Mathematics for Management | 4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| 2 | Module 2 | DSM-102 | Business Economics, Environment and Regulatory Framework | 4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| 3 | Module 3 | DSM-103 | Introduction to Supply Chain Management and Logistics | 4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| 4 | Module 4 | DSM-104 |
Materials and Inventory in Supply Chain Management
|
4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| 5 | Module 5 | DSM-105 | Seminars and presentations | 4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| Semester II | ||||||
| 1 | Module 6 | DSM-106 |
Transportation, Warehousing and Freight Management
|
4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| 2 | Module 7 | DSM-107 |
Supply Chain Service Practice and Procedure
|
4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| 3 | Module 8 | DSM-108 | Global Supply Chain, Export Trade and documentation | 4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| 4 | Module 9 | DSM-109 |
Computer Application in Supply Chain Management
|
4/4 | 60 | 40/60 |
| 5 | Module 10 | DSM-110 | Industrial Training, project report, and presentation | 22/32(12+8+2) | 360 | 300 |
| Total credits | 60/40 | 900 | 1200 | |||
Semester I
DSM-101 Accounting and Mathematics for Management
Unit 1: Introduction of Accounting
Financial Accounting-concept, importance and scope, accounting principles, journal, ledger, trial balance
Unit 2: Preparation of Final Accounts
Trading account, Profit and Loss account, Preparation of Balance sheet, depreciation (straight line and diminishing balance methods)
Unit 3: Analysis of Financial Statements
Comparative Balance Sheet- Income Statement, Common Size Statements, Ratio Analysis and Cash Flows Statements
Unit 4: Preparation of cost sheet
Stores Control – ECQ-Maximum, Minimum, Reordering Levels – Pricing of Materials Issues – problems ( FIFO, LIFO, and AVERAGE COST methods only) – labour cost – remuneration and incentives – problems. Standard Costing – Variance Analysis – problems (Material and Labour Variances only) – Marginal Costing – Cost Volume Profit analysis. Budgeting – preparation of various budgets.
Unit 5: Mathematics of Finance
simple and compound interest – TVM (Time Value of Money) concept of Annuity, compounding & discounting technique
Suggested Readings
- Gupta, RL and Radhaswamy, M : Financial Accounting ; Sultan Chand and Sons
- Ashoke Banerjee: Financial Accounting,Excel Books
- Maheshwari:Introduction to Accounting,Vikas Publishing
- Agarwala, AN, Agarwala KN: Higher Sciences of Accountancy : Kitab Mahal
- Anthony, RN and Reece, JS : Accounting Principles; Richard Inwin Inc
- Ramchandran & Kakani : Financial Accounting for Managers; Tata McGraw-Hill
- Grewal, T.S. : Double Entry Book Keeping
- Jain and Narang : Advanced Accountancy
- Gupta R.L. : Advanced Accountancy
- Jain and Narang : Cost Accounting
- Nigam and Sharma : Cost Accounting
DSM-102 Business Economics, Environment and Regulatory Framework
Unit 1 Introduction
Concepts, Economics, Business Management, Business Decisions. Managerial Economics: Profit Management, Nature & Measurement of Profit; Profit Planning and Control; Policies on Profit and Maximization. Fiscal and Monetary Policies: IS-LM Framework; Theory of Business; Cycle-Stabilization policy.
Unit 2 Marginal Analysis
Break-Even analysis for managerial decision making. Economic Concepts: Competitive Advantage; Exchange Rates; Trade Restrictions, BOP, WTO. Indian Economic Overview
Unit 3 Indian Business Environment
Concept, components and importance. Economic Trends: Income; Savings and investment; Industry; Trade and Balance of Payments, Money; Finance; Prices. Role of Government: Monetary and fiscal policy; Industrial licensing, Privatization; Devaluation; Export-import policy; Regulation of foreign investment; Collaborations in the light of recent changes. Industrial Policy: Industrial Policies since Independence, New Industrial Policy and its Effect. The Current Annual Plan and Niti Aayog: Major policies; Resource allocation.
Unit 4 Law of Contract
Nature of contract; Classification; Offer and acceptance; Capacity of parties to contract; Free consent; Consideration; Legality of object; Agreement declared void; Performance of contract; Discharge of contract; Remedies for breach of contract. Special Contracts: Indemnity; Guarantee; Bailment and pledge; Agency. Sale of Goods Act : Formation of contracts of sale; Goods and their classification, price; conditions and warranties; Transfer of property in goods; Performance of the contract of sales; Unpaid seller and his rights, sale by auction; Hire purchase agreement.
Unit 5 Negotiable Instrument Act
Definition of negotiable instruments; Features; Promissory note; Bill of exchange & cheque; Holder and holder in the due course; Crossing of a cheque, Types of crossing; Negotiation; Dishonour and discharge of negotiable instrument. The Consumer Protection Act: Salient features; Definition of consumer; Grievance redressal machinery. Foreign Exchange Management Act: Definitions and main provisions
Suggested Readings
- Adhikary, : Business Economics, Excel Books
- Thomas, : Managerial Economics, Tata McGraw Hill
- Mithani M: A course in Business Economics,Himalaya Publishing
- Dubedi: ,Principles of Economics,Vikas Publishing
- Dutt R and Sundharam KPM: Indian Economy; Chand
- Misra SK and Puri VK: Indian Economy; Himalaya Publishing
- Upadhyay, S: Business Environment, Asia Books
DSM-103 Introduction to Supply Chain Management and Logistics
Unit 1: Concept of supply chain
Integrated supply chain, Growth of Supply chain, Strategic decision in supply chain Definition of Supply Chain Management, Scope, Supply Chain Management as a Management Philosophy, Function of SCM, Why Supply Chain Management, and Value chain for Supply Chain Management.
Unit 2: Customer focus in Supply Chain Management
Buyers Perspective, Suppliers Perspective, and Stages of Development in Supplier Relation. Supply Chain Strategies – (i) Cycle View (ii) Push & Pull View.
Achievement of strategic fit through different steps, Obstacles to achieving Strategic Fit. : Role of Forecasting in a supply chain, Factors of Demand Forecast, Basic approach to Demand Forecasting, Role of Aggregate Planning in a Supply Chain, Problems, Planning Strategies.
Unit 3 Definition of logistics
Decision in Logistics Management, Key Factors for efficient Logistic System, Total Logistics Cost. Evolution of Logistics Management, Models in Logistics Management, Logistics Management to Supply Chain Management, Logistics Management Process, Competitive advantage through Logistics
Unit 4 Impact of Logistics & Customer Services on Marketing
Service Driven Logistics System, Logistic Impact on Return Investment, Logistics and Shareholder value. The work of Logistics – Network Design, Information, Transportation, Inventory, Warehousing, Materials Handling & Packaging.
Integrated Logistics – Logistics Performance Cycles – Physical Distribution, Manufacturing Support, and Procurement Performance.
Unit: 5 Information Functionality and Principles of Logistics
Logistical Measurement Systems, Characteristics of an Ideal Measurement System, Logistics Value – engineering.
- Supply Chain Management – Sunil Chapra & Peter Meindl,
- PHI Essentials of Supply Chain Management – Dr. R.P. Mohanty & Dr. S.G. Deshmukh, Jaico Publishing House
- Designing & Managing The Supply ChainDavid Simchi-Levi , Philip Kamiusky, Edith Simchi-Levi, TATA Mc-Graw Hill Logistics & Supply Chain Management – Cases & Concepts; – G. Raghuram & N. Rangaraj, MACMILLAN
- Logistical Management – Donald. J. Bowersox & David J. Closs., Tata Mc Graw Hill
- Logistics & Supply Chain Management – Martin Christopher, Pearson
DSM-104 Materials and Inventory in Supply Chain Management
Unit 1 Integrated Materials Management
Need, scope, advantage, concept; materials requirement planning and budgeting; make or buy decision; ABC and VED analysis. Purchasing Management: Purchase system, policy and procedure; source selection, vendor development and evaluation; legal aspects of buying.
Unit 2 Stores Management
Stores system and procedures; stores accounting and stock verification; disposal of surplus and scrap. Inventory Control: Economic Ordering Quantity; inventory systems. Evaluation of Materials Management: MIS for materials management; criteria for evaluation; inventory turnover ratio.
Unit 3 Definition, Importance, Function, Classification of Inventory, Inventory related Cost, Objectives of Inventory Control, and Planning for Inventory Control, Types of Inventory Situations. Selective Inventory Control Model- ABC Analysis, EOQ Model, P & Q System, Concept of JIT.
Unit 4 Inventory Control Process – Perpetual Review, Periodic Review, Modified Control, Distribution Requirement Planning (DRP), Process of DRP, Benefits & limitation of DRP. Classification of W.I.P Inventories, Factors influencing, W.I.P inventory, Problems, Controlling Method.
Unit 5 Factors influencing Finished Goods inventory, Requirement of inventory control Systems, Multi echelon Inventory Model, Use of Information Technology in Inventory Management.
Suggested Readings
- Gopalakrishnan, and Sunderashan, M : Handbook of Materials Management, Prentice Hall of India.
- Mishra: Materials Management,Excel Books
- Nair: Purchase and Materials Management,Vikas
- Dutta, A.K. : Integrated Materials Management, Prentice Hall of India
- Bhattacharya, C. : Modern Concepts on Materials Management
- Dobler, W. & Others : Purchasing and Materials Management, McGraw Hill.
- Inventory Management – Shridhara Bhat, Himalaya Publishing House
- Logistical Management-The integrated Supply Chain Process –
- J. Bowersox & Donald. J. Claoss, TATA Mc-Graw Hill
- Inventory Management – C. Jhamb, Himalaya Publishing House
DSM105 Seminars and Presentations
Seminars and presentations will be conducted in the topics relevant to the course. The topics can be selected by students or can be the choice of the instructor
Semester II
DSM-106 Transportation, Warehousing and Freight Management
Unit 1 Transportation
Definition-Objectives-Principles-role of transportation in logistics transport functionality & Principles-participants in Transportation Decisions.
Unit 2 Mode of Transport
Rail, Road, Water, Air, Pipeline-their characteristics and their cost structure-The carrier selection decision-determinants of carrier selection-legal classification of carriers-Role of couriers as carriers.
Unit3 Intermodal transport
Definition-rationale-types-limitations-containerisation-piggyback ownership of transport-own account transport and third-party transport-choice of ownership factors to be considered. Transportation costs – fixed, variable, joint and common costs-product related & Market related factors influencing transport cost.
Unit 4: Warehousing
Definition-nature and importance-role of warehousing in logistic system- types-basic components-functions-warehousing layout and design-warehousing decisions & operations-warehouse productivity. Packaging-importance-advantages-objectives and principles-types of packaging materials used-Bar coding.
Unit 5: Freight structure and Practice
Freight rates-principles-contracts of freightments-Sea freight-meaning- Sea freight Rates-types. Conference liner Tariffs-basic principles to determine liner freight rates-Liner Freight rebate system-operations-factors to be considered-determinants of freight rates-Freight rate indices-Tramp Freights-Tramp Trade-Tramp Market and Freight Rates-Time for Payment-Types of Freight-Ship owners ‘Lien for freight.
Suggested Book
- David J. Bloomberg, Stephen LeMay & : Logistics, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt Ltd., Joe B. Hanna New Delhi, 2003.
- Donald J. Bowersox & David J. Closs : Logistical Management, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Ltd, New Delhi, 2004.
- Satish C. Ailawadi & Rakesh Singh : Logistics Management, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2005.
- Donald Waters: Logistics. Palgrave Macmillan, New York, 2004.
- Krishnaveni Muthiah : Logistics Management & World Sea borne Trade, Himalaya Publishing 6. House, Mumbai, 1999.
- Sarika Kulkarni : Supply Chain Management, Tata Mc- Ashok Sharma Graw Hill Publishing Co Ltd., New Delhi, 2004
DSM-107 Supply Chain Service Practice and Procedure
Unit 1 Customer Service
Availability, Operational Performance, Service Reliability, basic Service Platforms, and value-added services. The role of cycle inventory in supply chain, Economics of Scale to exploit –Fixed cost, Quantity Discounts. The Role of Safety Stock in Supply chain. Determining the appropriate level of safety stock
Unit 2 purchasing and Supply Management
Introduction-importance Objectives purchasing process- purchasing & other functions-Purchasing and integrated logistics interfaces-Types of purchases-Purchasing Partnerships-Materials sourcing-Just-in-time purchasing. The Role of Sourcing in Supply Chain, Supplier scoring & assessment, Sourcing Planning & analysis, Making Sourcing decisions in Practice
Unit 3 The Role of Revenue Management in the Supply chain
Revenue Management for Multiple customer Segments, Revenue Management for –Perishable Asset, Seasonal Demand, Bulk & Spot contracts. Supply chain Integration-Stages-Barriers to internal integration-Achieving Excellence in SCM- Dimensions of Supply Chain Excellence-Forces influencing SCE Emotions, Physical and Financial Supply Chains-Check list for Excellence
Unit 4 Benchmark in Supply Chain
Product, Process, Best Practices, Strategic etc. Steps in Benchmarking. Rule of critical Success factors. Determination of what to Benchmark.
Unit 5 Performance Measurement in SCM
Meaning-Advantages of performance measures-The benefits of performance measurement-Measuring SCM-Supplier performance measurement- Parameters choosing suppliers.
Suggested Books:
- Supply Chain Management: —-Sunil Chopra & Peter Meindl (PHI)
- Essentials of Supply Chain Management: —–Dr. R.P Mohanty & Dr. S.G. Deshmukh (Jaico student edition)
- Supply Chain Management, Sarika Kulkarni, Tata Mc- Graw Hill Publishing Co Ltd., New Delhi, 2004.
- Logistical Management, Donald J. Bowersox & David J. Closs, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Ltd, New Delhi, 2004
- Logistics Management, Satish C. Ailawadi & Rakesh Singh, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2005
DSM-108 Global Supply Chain, Export Trade and documentation
Unit 1 Introduction
Forces of Global Supply Chain-Global market force, Technology force, Global cost force, Political force. Stage of International Development. Risk of Global Supply Chain- Speculative Strategies, Hedge Strategies, Flexible Strategies, Requirements for Global Strategy implementation, Advantages of Global Supply Chain. Supply Chain security.
Unit 2 Issues in international Supply Chain Management
International Versus Regional Product, Local autonomy versus control logistics –Importing & Exporting, Main forces, barriers The Global Supply Chain-Performance Cycle length, operations, system integration, Alliances, Views of Global Logistics –Importing & Exporting, Main force.
Unit 3 Exporting Preliminary Consideration
Generation of Foreign enquiries, obtaining local quotation & offering to overseas buyers scrutinizing export order, opening L/C by buyers- Export Controls and Licenses –Patent, Trade Mark, Copy Right Registrations- Confidentiality and NDA
Export Sales – Selling and Purchasing- Consignment – Leases – Marine and Air Causality Insurances – Export Finance – Forex – Major currencies, Exchange rates, relations & impact – Export costing and pricing & Incoterms – Export Licence – Import Licence
Unit 4: Export Packaging
Preparation of pre shipment documentation – Methods of Transportation – Country of Origin Marking- Inspection of Export consignment – Export by Post, Road, Air & Sea – Claiming for Export benefits and Duty drawbacks
Unit 5: Shipment & Shipping documents
Complicated problems in shipments & negotiation of shipping documentations – Corporate marketing strategies – 100% EOU & Free trade zone – Deemed Export –Isolated Sales Transactions
Suggested Readings
- Supply chain Management- Sunil Chopra & PeterMeindl(PHI)
- Logistical Management – Donald J. Bouersoxand David closs (TATA MC GRAW HILL)
- Essentials of Supply Chain Management- Dr. P.Mohanty & Dr. S.G.Deshmukh (Jaico Student Edition)
- Export Import Procedures- Documentation and Logistics, Publisher: New Age International, By: Shri C Rama Gopal, Chartered
- Export Management, P K Khurana
- Export Import Management, Justin Paul & Rajiv Aserkar
DSM109 COMPUTER APPLICATION IN SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Unit 1: Introduction to Computer System
Basic Computer Organization: Introduction, features and capabilities, components of computer system, classification of computers; Applications of Computers in Merchandising Business.
Unit 2: MS Word
Features, Creating, Saving and Opening Documents in Word Advanced Features of MS Word, Find & Replace, Using Thesaurus, Using Auto- Multiple Functions, Mail Merge, Handling Graphics, Tables & Charts
Unit 3: MIS Applications in Business Information Technology
Recent Developments in the Field of Information Technology: Hardware and Software, Data Communication Concepts and Internet, Centralized and Distributed Processing, Database, and Multimedia Applications.
Unit 4: MS-Excel
Worksheet basics, creating worksheet, heading information, data, text, dates, alphanumeric values, Opening and moving around in an existing worksheet, Toolbars and Menus, Working with single and multiple work-book. Working with formulae & cell referencing, Auto sum, coping formulae, Absolute & relative addressing, Worksheet with ranges, formatting of worksheet, Previewing & Printing worksheet, Graphs and charts, Database Creating and using macros.
Unit 5: Database Management System
Overview of DBMS; Components of DBMS. Concept, Characteristics, Objectives, MS Power Point: Creating slide show with animations.
Suggested Books
- Bharihoke, D. Fundamentals of Information Technology. New Delhi: Excel Books, 2009
- Norton, P. Introduction to Computers. New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill Publications, 2006
- RitendraGoel& D.N. Kakkar. Computer Applications in Management. New Delhi: New Age International (P) Ltd, 2004
DSM110- Industrial Training, project report, and presentation
Every candidate shall have to prepare a project study / dissertation under the supervision of a faculty member. The subject of project/dissertation shall be approved on the recommendations of the supervisor. A student shall be required to maintain record of periodic progress of the project. He / she should be in constant touch with his/her supervisor.
The candidate will prepare the report in consultation with the supervisor and the same shall be carry 60 marks. A viva-voce will be conducted on the completion of the dissertation. The viva-voce shall carry 40 marks